Published at May 11, 2023
4 min read
Communication in Distribute System
Issue in Client-Server communication
Addressing
- Hard-wired address: Machine address and process address are known
- Broadcast-base:
- server chooses address from a sparese address space
- Client broadcasts request
- Can cache response for future
- Using Nameserver
Blocking vs Non-blocking
-
Blocking communication is synchronous means:
- Send blocks until message is actually sent
- Receive blocks until message is actually received
-
Non-blocking communication is asynchronous:
- Send return immediately
- return does not block either
Buffered vs Unbuffered
- Unbuffered communication: server must call receive before client send
- Buffered communication:
- Client send to a mailbox
- Server receives from a mailbox
Reliable vs Unreliable
- Unreliable channel
- Need acknowledgements (ACKs)
- Application handle ACKs
- ACKs for both request and reply
- Reliable channel
- Reply acts as ACK for request
- Explicit ACK for repsonse
- Reliable communication on unreliable channels
- Transport protocol handles lost messages
Remote Procedure Calls (RPC)
What is RPC ?
- Goal: Make distributed computing look like centralized computing
- Allow remote services to be called as procedures
- Regardless of location, implemention, language
- Issues:
- How to pass parameters
- Bindings
- Sementics in face of errors
- Two classses: Integrated into prog, language and separate
Parameter passing
Local procefure passing by "callByValue" or "Call by reference". RPC simulate this through
- Stubs - Proxies: Take care of packaging arguments and sending messages, stub compiler generates stubautomatically from specs in an IDL (Interface Definition Language)
- Flattening - Marshalling: packaging parameters
Steps
- Client procedure calls client stub
- CLient Stubs builds message, calls local OS
- client's OS sends message to Server's OS
- Server's OS give message to server Stub
- Server Stub unpacks parameters, call server
- Server does work, return result to stub
- Repeat the steps to send message to Client
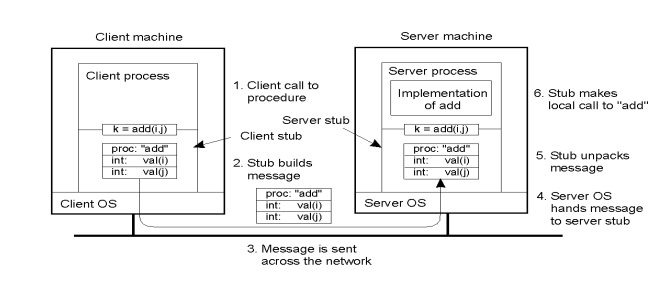
Marshalling
- Standard Representation (Ex: XDR, ...)
- Passing pointer
- If point to well defined data structure, pass a copy and stub poasses pointer to local copy
- Prohibit data structures containing pointers
- Transform parameters/results into a byte stream
Binding
Server: export server interface during initialization. Also, send name, version, unique identifier, handle (address) to binder Client: First RPC send message to binder to import server interface. Binder check server exported interface and return [handle and unique identifier] to client
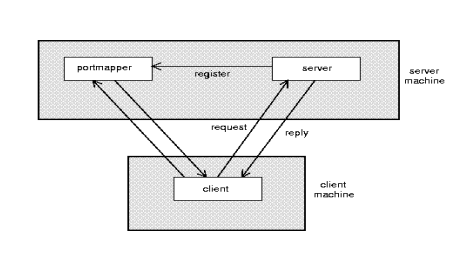
RPC models
- Lightweight RPCs: optimize for communicate between client and server but on same machine
- Push arguments onto stack
- Trap to kernel
- Kernel chanes mem map of client to server address space
- Client thread executes procedure (OS upcall)
- Thread traps to kernel upon completion
- Kernel changes the address space back and returns control to client
- Asynchronous RPC
- Deferred-synchronous RPC
- One-way RPC
RPC vs REST Api
Similarities
Both are API design approaches, allow two distinc services communicate without knowning detail knowledge about each others allow two distinc services communicate without detail knowledge about each others. + Abstraction: abstract lower level communications in network communications. + Communication medium: both use HTTP under the hood with JSON/XML,... + Multi-language Compatibility
Differences
- RPC focus more on functions or actions while REST focus on resources or objects (CRUD)
- RPC usually used for calling complicate actions/functions in remote server while REST usually used for action on objects (CRUD)
- RPC can be statefull or stateless while REST API must be stateless
- RPC is suitable for complicated task on remote services, REST is suitable when both client and server need to be uniform represented
- RPC parameters structure is defined by remote services while REST allow sending alternatives structure (JSON, XML, ...) clients have freedom to choose the data type they want
Conventional Procedure Call
- ...